What are RESTful APIs
The word REST stands for REpresentational State Transfer. In simple terms it's a pattern for creating an API. API stands for Application Programming Interface.
What is the use of REST API
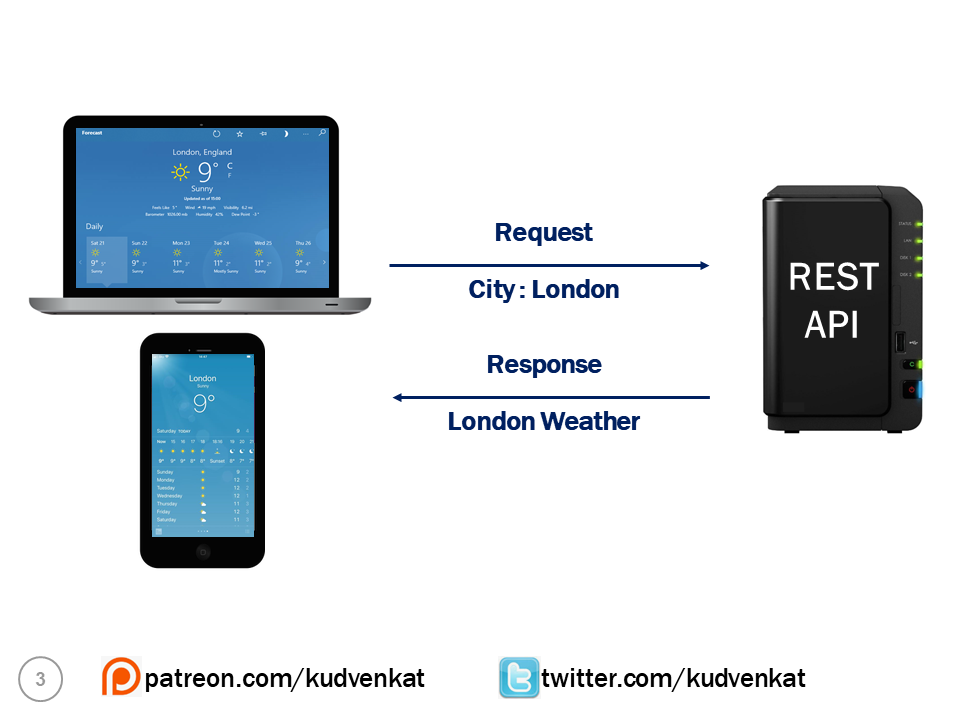
In simple terms a REST API allows applications to interact with each other and exchange data. For example, let's say you are building a mobile application or a web application. In that application you want to display weather data like temperature, humidity, wind speed etc.
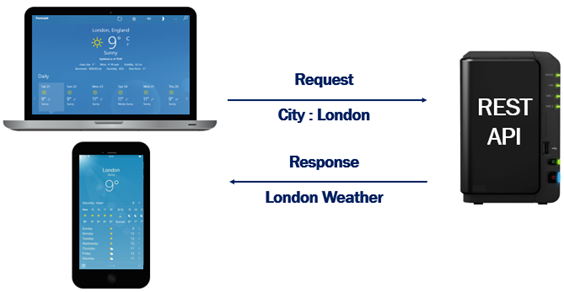
The problem is our application does not have this weather data. It is provided by a third party REST API service. Your application sends the city name for which you want weather data. The third party REST API sends weather data like temperature, humidity, wind speed etc back to your application.
Another REST API Example
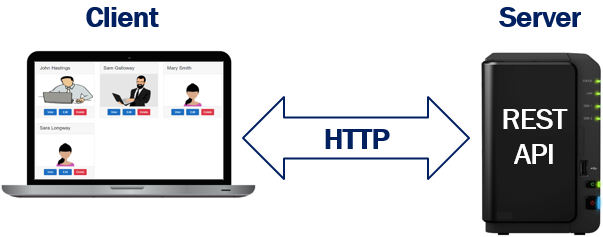
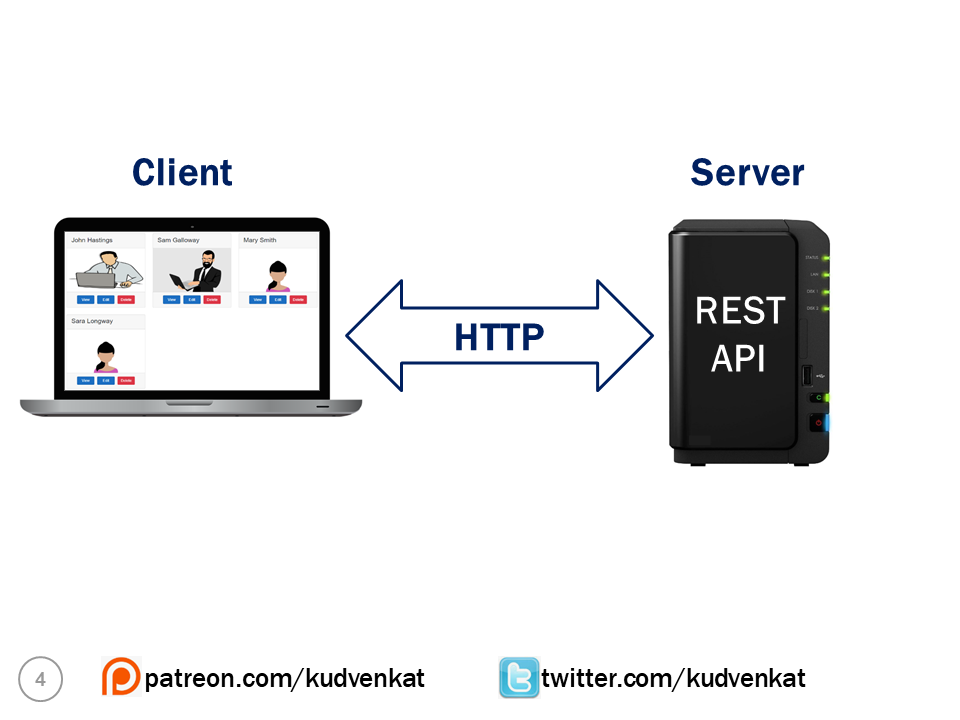
Let's say we are building an Employee portal. Employee data is provided to our application by a REST API. So here the employee portal is the client and the REST API that provides the employee data is the server. The communication between the client and the server happens over HTTP. If you want a more secure option you can also use HTTPS.
In this example, the client is a web application. Since REST is based on open standards, REST APIs can be consumed by a broad range of clients like
- Web Browsers
- Mobile applications
- Desktop applications
- IOTs i.e Internet Of Things.
REST Constraints
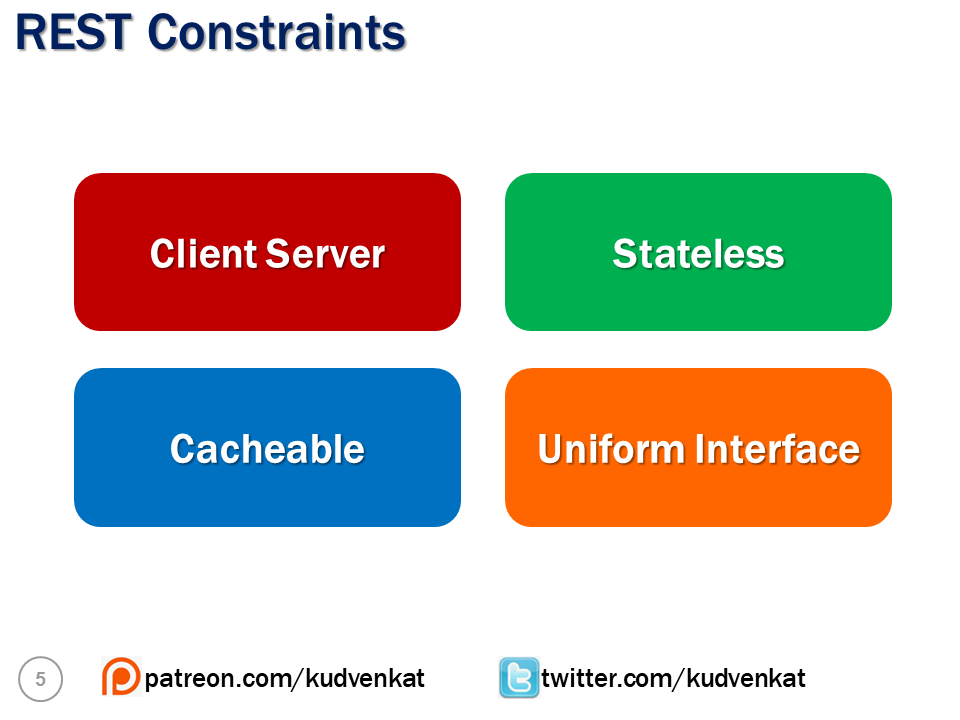
When building a REST API, we have to follow a set of rules. These are commonly called as REST Constraints. The following are some of the common REST constraints.
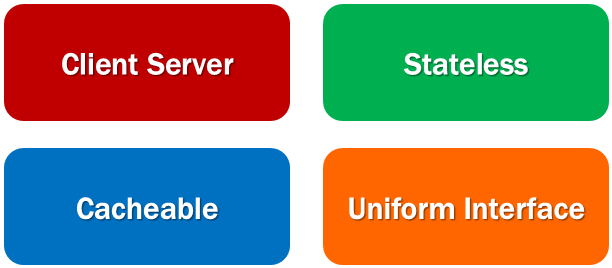
Client Server constraint
This is the first constraint. Client sends a request and the server sends a response. In our case Client is the Employee portal which sends a request for employee data and the server, the REST API, responds with employee data. This separation of concerns supports the independent evolution of the client-side logic and server-side logic.
Stateless constraint
The communication between the client and the server must be stateless between requests. This means we should not be storing anything on the server related to the client. The request from the client should contain all the necessary information for the server to process that request. This ensures that each request can be treated independently by the server.
Cacheable constraint
Some data provided by the server like list of products, or list of departments in a company does not change that often. This constraint says that let the client know how long this data is good for, so that the client does not have to come back to the server for that data over and over again.
Uniform Interface
As the name implies, this constraint defines the interface between the client and the server. This constraint helps us understand how a REST API actually works.
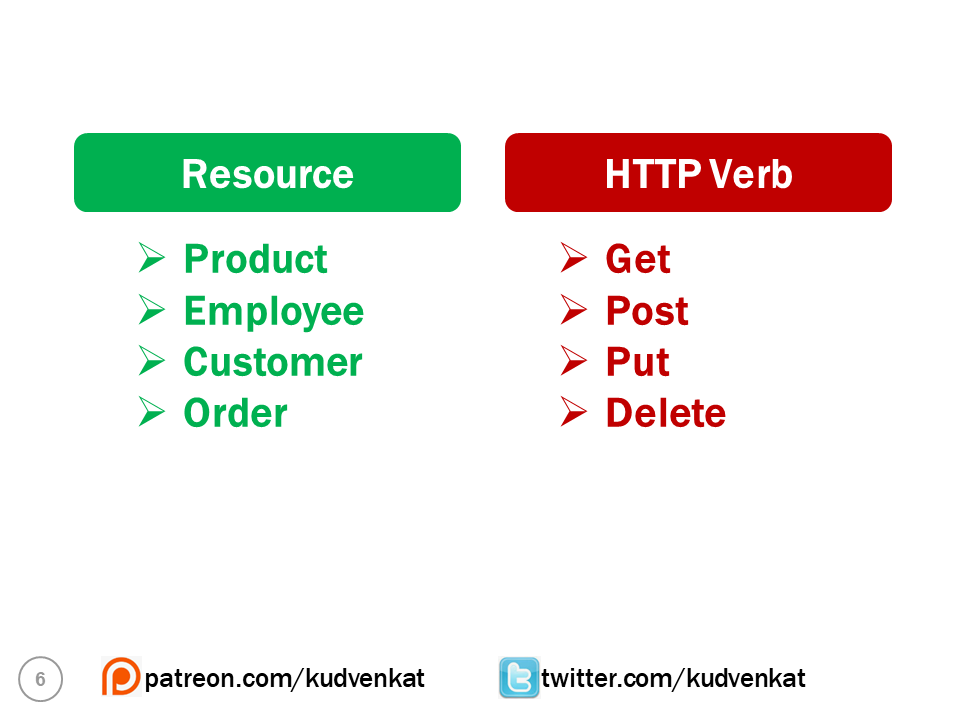
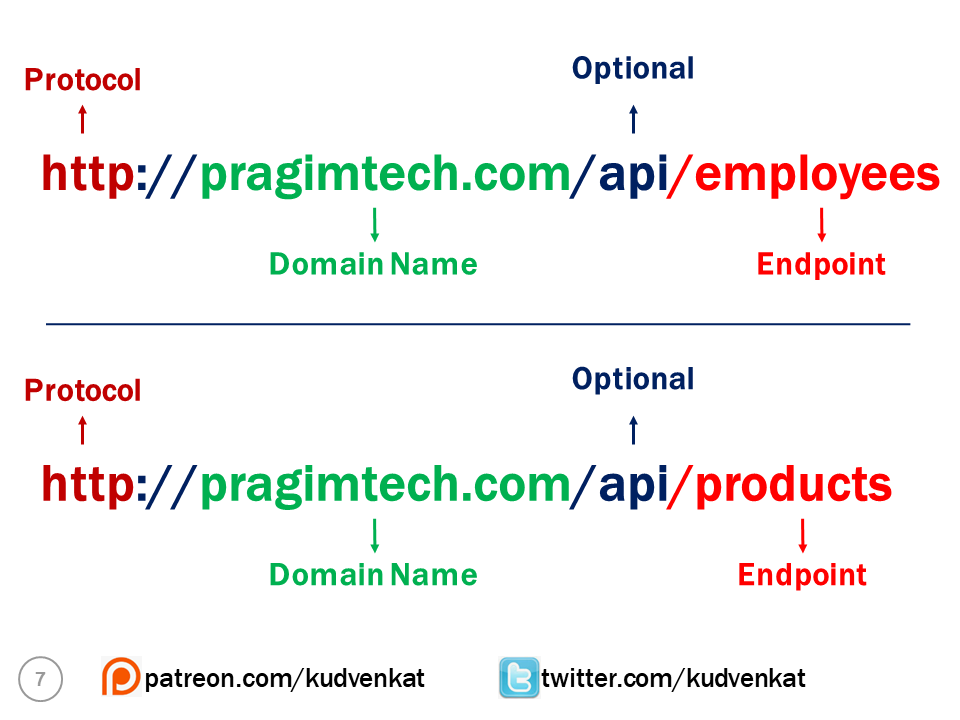
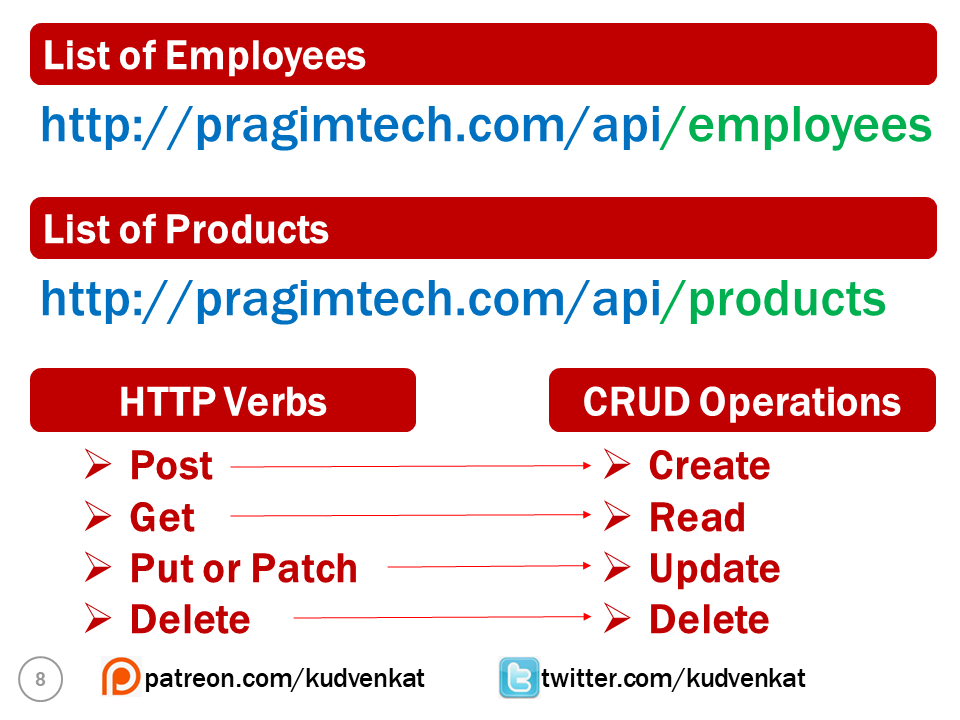
In the context of a REST API, a resource is a data entity like Product, Employee, Customer, Order etc. For example, a REST API that provides employee data makes the list of employees available at the following URI (Uniform Resource Identifier).

- The protocol that is used here is http. We can also use HTTPS to be a bit more secure.
- pragimtech.com is the domain.
- The path /api in the URI indicates that this is an API. This is just a convention that most people follow. With this convention just by looking at the URL, we can say this is a REST API URL.
- Finally /employees is the endpoint at which we have the resource i.e list of employees in this case.
If you have another resource like a product. Then the list of products might be available at the following end point

So, each resource, is identified by a specific URI. For example, the list of employees are available at the URI http://pragimtech.com/api/employees. Similarly, the list of products are available at the URI http://pragimtech.com/api/products.
Along with the URI, we also need to send an HTTP verb to the server. The following are the common HTTP verbs.
- GET
- POST
- PUT
- PATCH
- DELETE
It is this HTTP verb that tells the API what to do with the resource. The following are the 4 common operations that we do on any resource. For example, we create a new employee. EDIT, UPDATE or DELETE an existing employee.
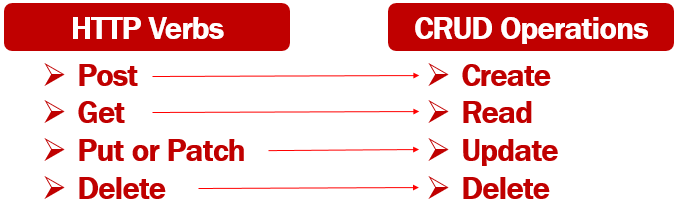
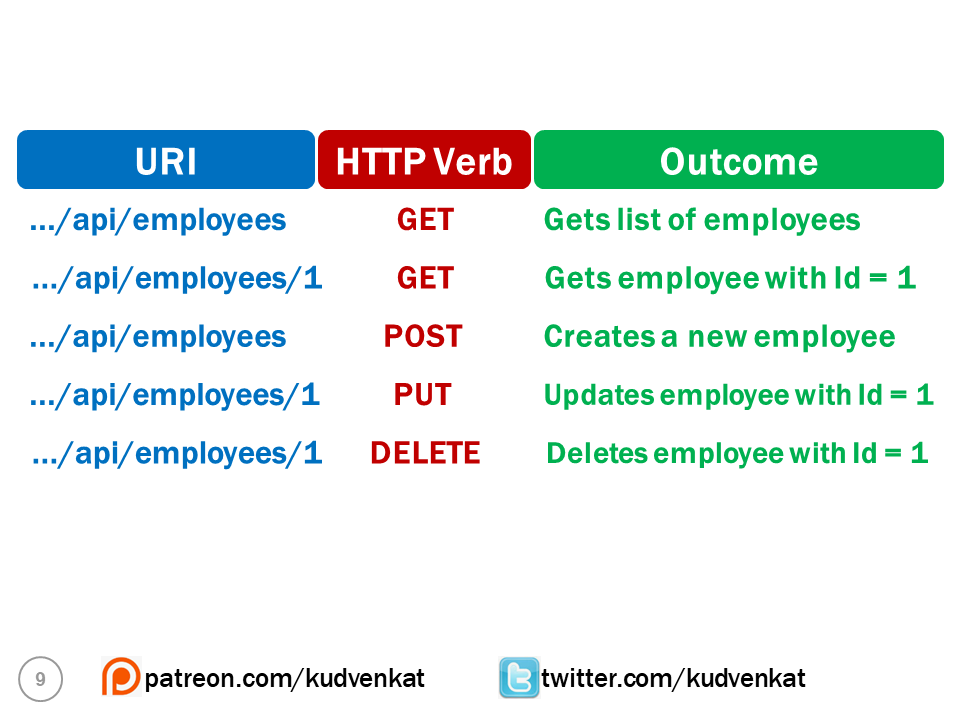
So the combination of the URI and the HTTP verb, that is sent with each request tells the server (i.e the REST API) what to do with the resource. For example,
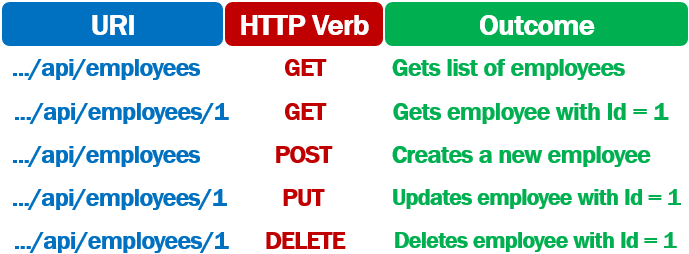
Remember a REST API must adhere to Stateless constraint. According to this constraint, the communication between the client and the server must be stateless i.e the request from the client must contain all the required information for the server to process that request.
So, when creating a new employee, the request
- Contains the URI .../api/employees
- The HTTP Verb - POST
- The employee object itself in the body of the request
Similarly to update an existing employee, the request
- Contains the URI .../api/employees/1. The id of the employee whose data we want to update is 1.
- The HTTP Verb - PUT
- The employee object that contains the changes is sent in the body of the request
PUT V/S PATCH
PUT updates the entire object i.e FirstName, LastName, DOB, Gender, Email etc of an employee. Basically all the properties of the object are updated.
PATCH is used when you want to do a partial update i.e only a subset of the properties. May be just FirstName and Gender of an employee object.
Slides
© 2020 Pragimtech. All Rights Reserved.

